Aim: How do we map the surface of the Earth?
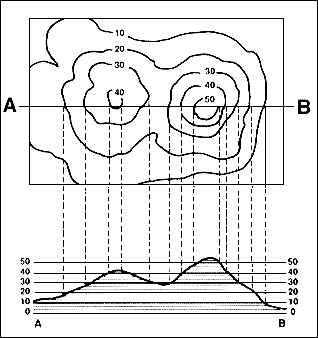
A profile is a picture of what the landscape would look like from the side. It is a cross section of the landscape. You should be able to identify a correct profile, as well as draw one.
A profile is a picture of what the landscape would look like from the side. It is a cross section of the landscape. You should be able to identify a correct profile, as well as draw one.
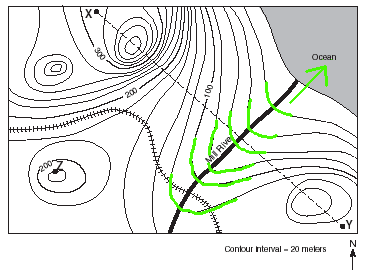
Given the topographic map above, which of the four choices below accurately depicts the correct profile between points X and Y?
Easy Peazy Steps to Constructing a Topographic Map Profile:
a. Lay a strip of paper along a line across the area where the profile is to be constructed.b. Mark on the paper the exact place where each contour, stream and hill top crosses the profile line.
c. Label each mark with the elevation of the contour it represents.
d. Prepare a vertical scale on profile paper by labeling the horizontal lines corresponding to the elevation of each index contour line.
e. Place the paper with the labeled contour lines at the bottom of the profile paper and project each contour to the horizontal line of the same elevation.
f. Connect the points.